Medicine Case Discussion
Online blended bimonthly assignment toward summative assessment for the month of May 2021
Name: Lakshmi Manvitha Yechuri
Roll no: 169
May 30 2021
I have been given the following cases to solve in an attempt to understand the topic of 'Patient clinical data analysis' to develop my competency in reading and comprehending clinical data including history, clinical findings, investigations and diagnosis and come up with a treatment plan.
This is the link of the questions asked regarding the cases:
Below are my answers to the Medicine Assignment based on my comprehension of the cases.
1.PULMONOLOGY.
CASE 1
A 55 Year Old Female with Shortness of Breath, pedal Edema and Facial Puffiness.
Question 1.
What is the evolution of the symptomatology in this patient in terms of an event timeline and where is the anatomical localization for the problem and what is the primary etiology of the patient's problem?
Answer: EVOLUTION OF SYMPTOMATOLOGY
•1st episode of sob - 20 yr back
•2nd episode of sob - 12 yr back
•From then she has been having yearly episodes for the past 12 yrs
•Diagnosed with diabetis - 8yrs back
•Anemia and took iron injections - 5yr ago
•Generalised weakness - 1 month back
•Diagnosed with hypertension - 20 days back
•Pedal edema - 15 days back
•Facial puffiness- 15 yrs back
ANATOMICAL LOCATION OF PROBLEM: LUNGS
PRIMARY ETIOLOGY OF PATIENT:
Question 2:
what are the mechanism of action indication and efficacy over placebo of each of the phramacological and nonphramacological interventions used for this patient?
Answer:
1. HEAD END ELEVATION:
MECHANISM OF ACTION:
✓Improves oxygenation.
✓ Decreases incidence VAP
✓ Increase hemodynamic performance ✓Increase end expiratory Lung volume
✓ Decrease incidence of aspiration
INDICATIONS:
Meningitis, Head injury, Pneumonia
2. OXYGEN INHALATION TO MAINTAIN SPO2 ABOVE 92%
3.BiPAP : assist ventilation by delivering positive expiratory and inspiratory pressure with out need for ET incubation9
4.AUGMENTIN (Amoxicillin,clavulinic acid)
Mechanism of Action
Amoxicillin binds to penicillin-binding proteins within the bacterial cell wall and inhibits bacterial cell wall synthesis. Clavulanic acid is a β-lactam, structurally related to penicillin, that may inactivate certain β-lactamase enzymes.
5. AZITHROMYCIN
Azithromycin binds to the 23S rRNA of the bacterial 50S ribosomal subunit. It stops bacterial protein synthesis by inhibiting the transpeptidation/translocation step of protein synthesis and by inhibiting the assembly of the 50S ribosomal subunit.
6.LASIX( FUROSEMIDE)
Furosemide works by blocking the absorption of sodium, chloride, and water from the filtered fluid in the kidney tubules, causing a profound increase in the output of urine.
7.HYDROCORTISONE.
Hydrocortisone binds to the glucocorticoid receptor leading to downstream effects such as inhibition of phospholipase A2, NF-kappa B, other inflammatory transcription factors, and the promotion of anti-inflammatory genes.
8. IPRAVENT:
Ipravent belongs to a group of medicines known as anticholinergic bronchodilators. Anticholinergic bronchodilators work by relaxing the bronchial tubes (air passages) that carry air in and out of your lungs. This makes breathing less difficult.
9.PANTOP (PANTAPRAZOLE)
pantoprazole inhibit the final step in gastric acid production. In the gastric parietal cell of the stomach, pantoprazole covalently binds to the H+/K+ ATP pump to inhibit gastric acid and basal acid secretion.
Question 3:
WHAT COULD BE THE CAUSES OF HER SUDDEN EXACERBATION?
Answer:
As the lungs tend to be vulnerable organs due to their exposure to harmful particles in the air, several things can cause an acute exacerbation of COPD:
Respiratory infection, being responsible for approximately half of COPD exacerbations. Approximately half of these are due to viral infections and another half appears to be caused by bacterial infections.[6] Common bacterial pathogens of acute exacerbations include Haemophilus influenzae, Streptococcus pneumoniae and Moraxella catarrhalis.[7] Less common bacterial pathogens include Chlamydia pneumoniae and MRSA.[7] Pathogens seen more frequently in patients with impaired lung function (FEV<35% of predicted) include Haemophilus parainfluenzae (after repeated use of antibiotics), Mycoplasma pneumoniae and gram-negative, opportunistic pathogens like Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Klebsiella pneumoniae.[7]
Allergens, e.g., pollens, wood or cigarette smoke, pollution[5]
Toxins, including a variety of different chemicals[5]
Air pollution[citation needed]
Failing to follow a drug therapy program, e.g. improper use of an inhaler[citation needed]
In one-third of all COPD exacerbation cases, the cause cannot be identified.[citation needed]
Question 4:
Could the ATT have affected her symptoms? If so how?
Answer:.
Yes ATT affected her symptoms
Isoniazid and rifampcin -nephrotoxic - raised RFT was seen
Question 5:.
What could be the causes for her electrolyte imbalance?
Answer:
Answer :
Imbalance in serum electrolytes has been proved in patients with COPD, in both acute exacerbation and during stable disease [7].
Hyponatremia in patients with COPD developed secondary to many reasons, such as development or worsening of hypoxia, hypercapnia, and respiratory acidosis, and right-side heart failure with development of lower limb edema, renal insufficiency, use of diuretics, Syndrome of Inappropriate Antidiuretic Hormone Synthesis, malnutrition, and poor intake during acute exacerbations are common contributing factors in such patients. Activation of the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system and inappropriately elevated plasma arginine vasopressin in COPD may aggravate the electrolyte imbalance imbalance during acute exacerbation of COPD
2. NEUROLOGY
CASE 2
A 40year old male presented with chief complaints of irrelevant talking and decreased food intake since 9days.
Question 1:
What is the evolution of the symptomology in this patient in terms of an event timeline and where is the anatomical localization for the problem and what is the primary etiology of the patient's problem?
Answer
The patient is a chronic alcoholic, he drinks about 3-4quarters/day.he had developed seizures following the cessation of alcohol for 24hours it is due to the following reason:-alcohol affects the way in which nerve cells communicate. receptors are specialized proteins on the surface of nerve cells that receive chemical signals from one another. With long-term alcohol consumption, receptors affected by alcohol undergo adaptive changes in an attempt to maintain normal function.
Two important brain communication systems affected by alcohol involve the neurotransmitters:gamma-aminobutyric acid and glutamate.
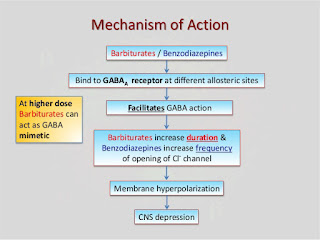
The GABA system:
GABA is an inhibitory neurotransmitter that helps to regulate brain function by rendering nerve cells less sensitive to further signaling. single doses of alcohol facilitate the inhibitory function of the GABA receptor, contributing to alcohol intoxicating effects. During withdrawal, brain GABA levels fall below normal and GABA activity declines. The combination of reduced brain GABA levels and GABAa receptor sensitivity may be contributed an adaptation to the presence of alcohol. In the absence of alcohol, the resulting decrease in inhibitory function may contribute to Symptoms of nervous system hyperactivity associated with both acute and protracted AW.
The glutamate system:
The major excitatory neurotransmitter in the brain is glutamate, which communicates with three major subtypes of glutamate receptors. Among these, the N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) receptor plays a role in memory, learning, and the generation of seizures. Alcohol inhibits the excitatory function of the NMDA receptor in laboratory studies at concentrations associated with mild to moderate alcohol intoxication in humans. As with the increased inhibitory function of the GABAA receptor, the decreased excitatory function of the NMDA receptor is consistent with alcohol’s general sedative effect. Long-term alcohol administration produces an adaptive increase in the function of NMDA receptors. Acute AW activates glutamate systems. In turn, AW seizures are associated with increased NMDA receptor function. Persistent alterations in NMDA receptor function may potentiate the neurotoxic and seizure-inducing effects of increased glutamate release during withdrawal.
The symptom: irrelevant talking, decreased food intake, tremors, sleep disturbance is due to the following reason: chronic alcohol consumption causes thiamine deficiency due to impaired absorption of thiamine from the intestine, a possible genetic predisposition, inadequate diet, reduced storage of thiamine in the liver and other nutritional deficiencies.
THE PATHOPHYSIOLOGY:
Thiamine, one of the first B vitamins to be discovered also known as Vitamin B1, is a coenzyme that is essential for intricate organic pathways and plays a central role in cerebral metabolism. This vitamin acts as a cofactor for several enzymes in the Krebs cycle and the pentose phosphate pathway, including alpha-keto-glutamic acid oxidation and pyruvate decarboxylation. Thiamine-dependent enzymes function as a connection between glycolytic and citric acid cycles.
Therefore, deficiency of thiamine will lead to decreased levels of alpha-keto-glutarate, acetate, citrate, acetylcholine and accumulation of lactate and pyruvate. This deficiency can cause metabolic imbalances leading to neurologic complications including neuronal cell death. Neuronal death in the mammillary bodies and thalamus were implicated in multiple cases of Wernicke encephalopathy studied. Studies involving computed tomography (CT) and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) of patients with Wernicke encephalopathy revealed lesions in the thalamus with dilated ventricles and volume loss in the mammillary bodies. The lesions are usually symmetrical in the midbrain, hypothalamus, and cerebellum.
The kidneys have an important job as a filter for harmful substances .alcohol causes changes in the function of the kidneys and makes them less able to filter the blood .alcohol also affects the ability to regulate fluid and electrolytes in the body. In addition, alcohol can disrupt hormones that disrupt hormones that affect kidney function .people who drink too much are more likely to have high blood pressure. High blood pressure is a common cause of kidney disease. The increase in levels of urea, creatinine, uric acid leads to uraemic encephalopathy. which causes asterixis.
the deficiency of thiamine and increase in levels of toxins in the body due to renal disease is the primary etiology of the patient's problem.
Question 2:
What are the mechanism of action, indication, and efficacy over placebo of each of the pharmacological and nonpharmacological interventions used for this patient?
Answer
Thiamine helps the body cells change carbohydrates into energy. It has been used
i)as a supplement to cope with thiamine deficiency
ii)Lorazepam binds to benzodiazepine receptors on the postsynaptic GABA-A ligand-gated chloride channel neuron at several sites within the central nervous system.it enhances the inhibitory effects of GABA, which increases the conductance of chloride ions into the cell
iii)pregabalin subtly reduces the synaptic release of several neurotransmitters, apparently by binding to alpha2-delta subunits, and possibly accounting for its actions invivo to reduce neuronal excitability and seizures.
iv)Lactulose is used in preventing and treating clinical portal-systemic encephalopathy .its chief mechanism of action is by decreasing the intestinal production and absorption of ammonia.
v)Potchlor liquid is used to treat low levels of potassium in the body.
Question 3:
Why have neurological symptoms appeared this time, that were absent during withdrawal earlier ? what could be a possible cause for this time?
Answer
Due to excess thiamine deficiency and excess toxins accumulation due to renal disease caused by excess alcohol addiction.
Question 4:
What is the reason for giving thiamine in this patient?
Answer
chronic alcohol consumption causes thiamine deficiency due to impaired absorption of thiamine from the intestine,Thiamine, one of the first B vitamins to be discovered also known as Vitamin B1, is a coenzyme that is essential for intricate organic pathways and plays a central role in cerebral metabolism. This vitamin acts as a cofactor for several enzymes in the Krebs cycle and the pentose phosphate pathway, including alpha-keto-glutamic acid oxidation and pyruvate decarboxylation. Thiamine-dependent enzymes function as a connection between glycolytic and citric acid cycles. Therefore, deficiency of thiamine will lead to decreased levels of alpha-keto-glutarate, acetate, citrate, acetylcholine, and accumulation of lactate and pyruvate. This deficiency can cause metabolic imbalances leading to neurologic complications including neuronal cell death.
Question 5
What is the probable cause for kidney injury in this patient?
Answer
The kidneys have an important job as a filter for harmful substances .alcohol causes changes in the function of the kidneys and makes them less able to filter the blood .alcohol also affects the ability to regulate fluid and electrolytes in the body. In addition, alcohol can disrupt hormones that disrupt hormones that affect kidney function .people who drink too much are more likely to have high blood pressure. High blood pressure is a common cause of kidney disease.
Question 6
What is the probable cause for the normocytic anaemia?
Answer
alcohol causes iron deficiency or iron overload due its affect on production of new blood cells organs i.e,bonemarrow and the metabolism of iron .alocohol causes a affect on progenitor cells of blood causing decreased WBC .RBC.alochol decreases iron absorption from intestine
Question 7
Could chronic alcohlism have aggravated the foot ulcer formation ?if yes and why ?
Answer
yes,As the patient is diabetic the chance of ulcer formation increases .in a patient of chronic alcoholic theimmune system is weak due to the affect on blood cells formation and iron absorption.due to this healing of an ulcer dampens.
CASE 3
A 52 year old male came to the hospital 2 days back presenting with slurring of speech and deviation of mouth that lasted for 1 day and resolved on the same day.
Question 1
What is the evolution of the symptomology in this patient in terms of an event timeline and where is the anatomical localization for the problem and what is the primary etiology of the patients problem?
Answer
Timeline of the patient is as follows-
7 days back- Patient gave a history of giddiness that started around 7 in the morning; subsided upon taking rest; associated with one episode of vomiting
4 days back- Patient consumed alcohol; He developed giddiness that was sudden onset, continuous and gradually progressive. It increased on standing and while walking.
H/O postural instability- falls while walking
Associated with bilateral hearing loss, aural fullness, presence of tinnitus
Associated vomiting- 2-3 episodes per day, non projectile, non bilious without food particles
Present day of admission- Slurring of speech, deviation of mouth that got resolved the same day
Anatomical location- There is a presence of an infarct in the inferior cerebellar hemisphere of the brain.
Etiology- Ataxia is the lack of muscle control or co-ordination of voluntary movements, such as walking or picking up objects. This is usually a result of damage to the cerebellum (part of the brain that controls muscle co-ordination)
Many conditions cause cerebellar ataxia- Head trauma, Alcohol abuse, certain medications eg. Barbituates, stroke, tumours, cerebral palsy, brain degeneration etc.
In this case, the patient has hypertension for which he has been prescribed medication that he has not taken. Stroke due to an infarct can be caused by blockade or bleeding in the brain due to which blood supply to the brain is decreased, depriving it of essential oxygen and nutrients. This process could’ve caused the infarct formation in the cerebellar region of the brain, thus causing cerebellar ataxia.
Question 2
What are the mechanism of action, indication and efficacy over placebo of each of the pharmacological and non pharmacological interventions used for this patient?
Answer
A) Tab Vertin 8mg-
This is betahistine, which is an anti- vertigo medication
MOA- It is a weak agonist on H1 receptors located on blood vessels of the inner ear. This leads to local vasodilation and increased vessel permeability. This can reverse the underlying problem.
Indications- Prescribed for balance disorders. In this case it is used due to patients history of giddiness and balance issues.
B) Tab Zofer 4mg-
This is ondanseteron- It is an anti emetic
MOA- It is a 5H3 receptor antagonist on vagal afferents in the gut and they block receptors even in the CTZ and solitary tract nucleus.
Indications- Used to control the episodes of vomiting and nausea in this patient.
C)Tab Ecosprin 75mg-
This is aspirin. It is an NSAID
MOA- They inhibit COX-1 and COX-2 thus decreasing the prostaglandin level and thromboxane synthesis
Indications- They are anti platelet medications and in this case used to prevent formation of blood clots in blood vessels and prevent stroke.
D) Tab Atorvostatin 40mg-
This is a statin
MOA- It is an HMG CoA reductase inhibitor and thus inhibits the rate limiting step in cholesterol biosynthesis. It decreases blood LDL and VLDL, decreases cholesterol synthesis, thus increasing LDL receptors in liver and increasing LDL uptake and degeneration. Hence plasma LDL level decreases.
Indications- Used to treat primary hyperlipidemias. In this case it is used for primary prevention of stroke.
E) Clopidogrel 75mg- It is an antiplatelet medication
MOA- It inhibits ADP mediated platelet aggregation by blocking P2Y12 receptor on the platelets.
Indications- In this case it decreases the risk of heart disease and stroke by preventing clotting
F) Thiamine- It is vitamin B1
It is naturally found in many foods in the human diet. In this case, the patient consumes excess alcohol- so he may get thiamine deficiency due to poor nutrition and lack of essential vitamins due to impaired ability of the body to absorb these vitamins.
Indications- Given to this patient mainly to prevent Wernickes encephalopathy- that can lead to confusion, ataxia and opthalmoplegia.
G) Tab MVT- This is methylcobalamin
Mainly given in this case for vitamin B12 deficiency.
Question 3
Did the patients history of denovo hypertension contribute to his current condition?
Answer
A cerebellar infarct is usually caused by a blood clot obstructing blood flow to the cerebellum. High blood pressure that is seen in hypertension (especially if left untreated) can be a major risk factor for the formation of cerebellar infarcts.
Increased shear stress is caused on the blood vessels. The usual adaptive responses are impaired in this case, thus leading to endothelial dysfunction in this case. High BP can also promote cerebral small vessel disease. All these factors contribute to eventually lead to stroke.
Question 4
Does the patients history of alcoholism make him more susceptible to ischaemic or haemorrhagic stroke?
Answer
Meta analysis of the relation between alcohol consumption and increased risk of stroke has mainly weighed in to the formation of two types- ischaemic and haemorrhagic stroke.
Ischaemic stroke- this is more common. This Is caused by a blood clot blocking the flow of blood and preventing oxygen from reaching the brain
Haemorrhagic stroke- occurs when an aneurysm bursts or when a weakened blood vessel leaks, thus causing cerebral haemorrhage
According to a Cambridge study, heavy drinkers have 1.6 more chance of intracerebral haemorrhage and a 1.8 increased chance of subaracnoid haemorrhage. The adverse effect on BP that is seen due to increased drinking is a major stroke risk factor and increase the risk of heart stroke.
Many studies show that with mild and moderate drinking . the risk of ischaemic stroke decreases due to decreased level of fibrinogen which helps in the formation of blood clots. However, heavy alcohol intake is associated with impaired fibrinolysis, increased platelet activation and increased BP and heart rate.
So In this case, his history of alcoholism, coupled with his hypertension definitely could be a causative factor of his current condition.
CASE 4
A 45 years old female ,house wife by occupation came to opd with chief complaints of palpitations,chest heaviness,pedal edema,chest pain,radiating pain along her left upper limb , generalized body weakness
Question 1
What is the evolution of the symptomatology in this patient in terms of an event timeline and where is the anatomical localization for the problem and what is the primary etiology of the patient's problem?
Answer
Evolution of symptoms :patient was normal 8 months back then developed b/l pedal edema which gradually progressed.
Aggerevated in sitting and standing position, relived on taking medication
*Palpitations :since 5days, sudden in onset which is more during night
Aggerevated by lifting heavy weights, speaking continuously
*Dyspnoea during palpitations (NYHA-3) since 5 days
*pain:since 6days, radiating along left upper limb, more during palpitations and relived on medication.
Chest pain associated with chest heaviness since 5 days
Anatomical localisation :
Palpitations
Dyspnoea(NYHA-3)
Pedal edema
Chest pain
Radiating pain along her left upper limb
Etiological agent :
*By localization, electrolyte imbalance (hypokalemia) causing the her manifestations like palpitations, chest heaviness, generalised body weak ness
*radiating pain along her left upper limb due to cervical spondylosis
Question 2
What are the reasons for recurrence of hypokalemia in her? Important risk factors for her hypokalemia?
Answer
Reason: recurrent hypokalemic periodic paralysis
Current risk factor:due to use of diuretics
Other risk factors
A) Abnormal loses:
Medications-diuretics, laxatives, enema, corticosteriods
Real causes- osmotic diuresis, mineralo corticoid excess, renal tubular acidosis, hypomagnesenemia
B) trance cellular shift : alkalosis, thyrotoxicosis, delirium tremans, head injury, Myocardial, ischemia, recurrent hypokalemic periodic paralysis
C) Inadequate intake: anorexia, dementia, stareation, total parental nutrition
D) psuedohypokalemia:delayed sample analysis, significant leukocytosis
Question 3
What are the changes seen in ECG in case of hypokalemia and associated symptoms?
Answer
changes seen in ECG :
Earliest change :decreased T-wave amplitude, ST depression, Twave - and inversion or flat;prolonged PR interval;presence of Uwaves
In Severe cases :ventricular fibrillation, rarely AV block
Symptoms of hypokalemia :
Weakness & fatigue, palpitations, muscle cramps & pain, anxiety, psychosis, depression, delirium.
CASE 5
A 55year old male patient came to opd with c/o altered sensorium and involuntary movements from 11pm and recurrent episodes of seizures since 5yrs.
Question 1
Is there any relationship between occurrence of seizure to brain stroke. If yes what is the mechanism behind it?
Answer
Occurrence of seizure due to brain stroke
Cells in the brain send electrical signals to one another. The electrical signals pass along your nerves to all parts of the body. A sudden abnormal burst of electrical activity in the brain can lead to the signals to the nerves being disrupted, causing a seizure. This electrical disturbance can happen because of stroke damage in the brain.
A seizure can affect you in many different ways such as changes to vision, smell and taste, loss of consciousness and jerking movements.
Mechanism of seizure activity
You’re more likely to have a seizure if you had a haemorrhagic stroke (bleed on the brain). Seizures can also be more likely if you had a severe stroke, or a stroke in the cerebral cortex, the large outer layer of the brain where vital functions like movement, thinking, vision and emotion take place.
Some people will have repeated seizures, and be diagnosed with epilepsy. The chances of this happening may depend on where the stroke happens in the brain and the size of the stroke.
There are several causes for early onset seizures after ischaemic strokes. An increase in intracellular Ca2+ and Na+ with a resultant lower threshold for depolarisation, glutamate excitotoxicity, hypoxia, metabolic dysfunction, global hypo perfusion and hyper perfusion injury ,(particularly after carotid end arterectomy) have all been postulated as putative neurofunctional aetiologies. Seizures after haemorrhagic strokes are thought to be attributable to irritation caused by products of blood metabolism. The exact pathophysiology is unclear, but an associated ischaemic area secondary to haemorrhage is thought to play a part. Late onset seizures are associated with the persistent changes in neuronal excitability and gliotic scarring is most probably the underlying cause. Haemosiderin deposits are thought to cause irritability after a haemorrhagic stroke. In childhood, post‐stroke seizures can occur as part of perinatal birth trauma.
Question 2
In the previous episodes of seizures, patient didn't
loose his consciousness but in the recent episode he lost his consciousness what might be the reason?
Answer
Normally the “consciousness system”—a specialized set of cortical-subcortical structures—maintains alertness, attention and awareness. Diverse seizure types including absence, generalized tonic-clonic and complex partial seizures converge on the same set of anatomical structures through different mechanisms to disrupt consciousness.
CASE 6
48 year old male with seizures and altered sensorium
Question 1
What could have been the reason for this patient to develop ataxia in the past 1 year?
Answer
The patient has minor unattended head injuries in the past 1 yr. Accoding to the CT scan, the patient has cerebral haemorrhage in the frontal lobe causing probably for the occurrence of Frontal love ataxia
Question 2
What was the reason for his IC bleed? Does Alcoholism contribute to bleeding diatheses ?
Answer
The patient has minor unattended head injuries. During the course of time the minor hemorrhages if present should have been cured on their own. But the patient is a chronic alcholic. This might have hindered the process of healing or might have stopped the healing rendering it to grow further more into 13 mm sized hemorrhages occupying Frontal Parietal and Temporal lobes
CASE 7
A 30 year old male patient with weakness of right upper limb and lower limb
Question 1
Does the patient's history of road traffic accident have any role in his present condition?
Answer
The closeness of facial bones to the cranium would suggest that there are chances of cranial injuries. Since the Zygomatic arch and Mandibular process is very close to the cranium, this might play a role in the patient's present condition
Question 2
What are warning signs of CVA?
Answer
Weakness or numbness of the face, arm or leg, usually on one side of the body
Trouble speaking or understanding
Problems with vision, such as dimness or loss of vision in one or both eyes
Dizziness or problems with balance or coordination
Problems with movement or walking
Fainting or seizure
Severe headaches with no known cause, especially if they happen suddenly
Question 3
What is the drug rationale in CVA?
Answer
Mannitol- Because of its osmotic effect, mannitol is assumed to decrease cerebral edema. Mannitol might improve cerebral perfusion by decreasing viscosity, and as a free-radical scavenger, it might act as a neuroprotectant.
Ecospirin
For the prevention of heart attack, stroke, heart conditions such as stable or unstable angina (chest pain) due to a blood clot.
Atrovas-Atorva 40 Tablet belongs to a group of medicines called statins. It is used to lower cholesterol and to reduce the risk of heart diseases. Cholesterol is a fatty substance that builds up in your blood vessels and causes narrowing, which may lead to a heart attack or stroke.
Rt feed RT feed is a nursing procedure to provide nutrition to those people who are either unable to obtain nutrition by mouth or are not in a state to swallow the food safely.
Question 4
Does alcohol has any role in his attack?
Answer
When the patient met with an accident there might be cranial damage which was unnoticed.
If so his occasional drinking may or may not have hindered the process of the minor hemorrhages getting healed and might have caused this condition
But since the patient is not a chronic alcoholic and so Alcohol might not have played any role.
Therefore it cannot be evaluated without further details
Question 5
Does his lipid profile has any role for his attack??
Answer
The inverse relationship between serum HDL-C and stroke risk . When taken together it seems clear that higher baseline levels of serum HDL-C lower the risk of subsequent ischemic stroke.
CASE 8
A 50 year old male with cervical myelopathy presented to hospital
Question 1
what is myelopathy hand?
Answer
There is loss of power of adduction and extension of the ulnar two or three fingers and an inability to grip and release rapidly with these fingers. These changes have been termed "myelopathy hand" and appear to be due to pyramidal tract involvement.
Question 2
what is finger escape?
Answer
Involuntary abduction of fifth finger caused due to unopposed action of extensor digiti MINIMI-WARTENBERG'S SIGN
Presence of weak finger adduction in cervical myelopathy is called - FINGER ESCAPE SIGN
Question 3
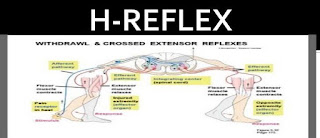
What is Hoffman's reflex
Answer
HOFFMANS REFLEX:It is reflectory reaction of muscles after electrical stimulation of type 1a sensory fibres(primary afferent fibres which constantly monitor the how fast a muscle stretch CHANGES) in their innervation nerves
H-REFLEX- is expression of of monosynaptic reflex, which runs in afferents from the muscle and back again through efferents of same muscles
A 17 year old female student by occupation presented to causality on 1/5/2021 with
Chief complaints of Involuntary movements of both upper and lower limbs a day before.
Question 1
What can be the cause of her condition ?
Answer
According to MRI cortical vein thrombosis might be the cause of her seizures.
Question 2
What are the risk factors for cortical vein thrombosis?
Answer
Infections:
Meningitis, otitis,mastoiditis
Prothrombotic states:
Pregnancy, puerperium,antithrombin deficiency proteinc and protein s deficiency,Hormone replacement therapy.
Mechanical:
Head trauma,lumbar puncture
Inflammatory:
SLE,sarcoidosis,Inflammatory bowel disease.
Malignancy.
Dehydration
Nephrotic syndrome
Drugs:
Oral contraceptives,steroids,Inhibitors of angiogenesis
Chemotherapy:Cyclosporine and l asparginase
Hematological:
Myeloproliferative Malignancies
Primary and secondary polycythemia
Intracranial :
Dural fistula,
venous anomalies
Vasculitis:
Behcets disease wegeners granulomatosis
Question 3
There was seizure free period in between but again sudden episode of GTCS why?resolved spontaneously why?
Answer
Seizures are resolved and seizure free period got achieved after medical intervention but sudden episode of seizure was may be due to any persistence of excitable foci by abnormal firing of neurons.
Question 4
What drug was used in suspicion of cortical venous sinus thrombosis?
Answer
Anticoagulants are used for the prevention of harmful blood clots.
Clexane ( enoxaparin) low molecular weight heparin binds and potentiates antithrombin three a serine protease Inhibitor to form complex and irreversibly inactivates factor xa.
3. CARDIOLOGY
CASE 10
A 78 year old male with shortness of breath, chest pain , bilateral pedal edema and facial puffiness.
Question 1
What is the difference btw heart failure with preserved ejection fraction and with reduced ejection fraction?
Answer
Preserved ejection fraction (HFpEF) – also referred to as diastolic heart failure. The heart muscle contracts normally but the ventricles do not relax as they should during ventricular filling (or when the ventricles relax).
Reduced ejection fraction (HFrEF) – also referred to as systolic heart failure
HFpEF is preceded by chronic comorbidities, such as hypertension, type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM), obesity, and renal insufficiency, whereas HFrEF is often preceded by the acute or chronic loss of cardiomyocytes due to ischemia, a genetic mutation, myocarditis, or valvular disease
Question 2
Why haven't we done pericardiocenetis in this pateint?
Answer
Pericardiocentesis is not done here Because the effusion was self healing ,It reduced from 2.4cm to 1.9 cm.
Question 3
What are the risk factors for development of heart failure in the patient?
Answer
risk factors for development of heart faliure in this patent
Alcohol abuse increases the risk of atrial fibrillation, heart attack and congestive heart failure
high blood pressure
Smoking
Diabetes
AV block can be associated with severe bradycardia and hemodynamic instability. It has a greater risk of progressing to third-degree (complete) heart block or asystole.
wosening of pericardial effusion leaing to cardiac tamponade.
Question 4
What could be the cause for hypotension in this patient
Answer
visceral pericardium may have thickened which is restricting the heart to expand causing hypotension
(May be secondary to TB)
CASE 11
A 73 year old male patient with pedal edema , shortness of breath and decreased urine output
Question 1
.What are the possible causes for heart failure in this patient?
Answer
1. The patient was diagnosed with type 2 diabetes mellitus 30 years ago and has been taking human mixtrad insulin daily and was also diagnosed with diabetic triopathy indicating uncontrolled diabetes which is major risk factor for heart failure
2. The patient was also diagnosed with hypertension 19 yrs. ago which is also a risk factor for heart failure
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/31472888/3. He is a chronic alcoholic since 40 years which is a risk factor towards heart failure
The findings in this article provide longitudinal evidence that moderate and heavy alcohol consumption are associated with decreased LVEF and trend towards a higher risk of incident LV systolic dysfunction, compared to light drinkers.
4. The patient has elevated creatinine and AST/ALT ratios is >2 and was diagnosed with chronic kidney disease stage IV. CKD is also one of the risk factors for heart failure
Question 2
what is the reason for anaemia in this case?
Answer
As he was chronic alcoholic, which impairs the production of precursors of RBC in bone marrow, also causes change in shape and functions of cells
Due to chronic kidney disease
Impaired renal clearance leading to decreased erythropoetin production-impaired production of rbc
Question 3
What is the reason for blebs and non healing ulcer in the legs of this patient?
Answer
As patient was diabetic, which impairs healing process leading to development of non healing ulcers
Due to chronic alcoholism leading to decreased production of proteins and clotting factors required for wound healing
Question 4
What sequence of stages of diabetes has been noted in this patient?
Answer
There are 4 stages in type 2 diabetes- insulin resistance, prediabetes, type 2 diabetes and type 2 diabetes and vascular complications, including retinopathy, nephropathy or neuropathy and, or, related microvascular events.
The patient is diagnosed with diabetic triopathy exhibiting sequence of neuropathy, retinopathy and nephropathy
The patient has been diagnosed with diabetic retinopathy, CKD stage IV and shows signs of diabetic neuropathy such as numbness
CASE 12
A 52yr old male came to the OPD with the chief complaints of decreased urine output and shortness of breath at rest since one day.
Question 1
What is the evolution of the symptomatology in this patient in terms of an event timeline and where is the anatomical localization for the problem and what is the primary etiology of the patient's problem?
Answer
the anatomical site is BLOOD VESSELS;
* ETIOLOGY:
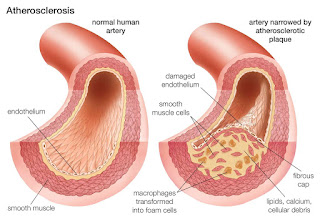
The physical stress of hypertension on the arterial wall also results in the aggravation and acceleration of atherosclerosis, particularly of the coronary and cerebral vessels. Moreover, hypertension appears to increase the susceptibility of the small and large arteries to atherosclerosis.
The most likely cause of arterial thrombosis is artery damage due to atherosclerosis. Atherosclerosis occurs when a person has a buildup of plaque on the walls of their arteries. The arteries then begin to narrow and harden, which increases a person's risk of developing arterial thrombosis.
Question 2
What are mechanism of action, indication and efficacy over placebo of each of the pharmacological and non pharmacological interventions used for this patient?
Answer
PHARMACOLOGICAL INTERVENTIONS
1. TAB. Dytor
mechanism: Through its action in antagonizing the effect of aldosterone, spironolactone inhibits the exchange of sodium for potassium in the distal renal tubule and helps to prevent potassium loss.
2. TAB. Acitrom
mechanism: Acenocoumarol inhibits the action of an enzyme Vitamin K-epoxide reductase which is required for regeneration and maintaining levels of vitamin K required for blood clotting
3. TAB. Cardivas
mechanism:Carvedilol works by blocking the action of certain natural substances in your body, such as epinephrine, on the heart and blood vessels. This effect lowers your heart rate, blood pressure, and strain on your heart. Carvedilol belongs to a class of drugs known as alpha and beta-blockers.
4. INJ. HAI S/C
MECHANISM:Regulates glucose metabolism
Insulin and its analogues lower blood glucose by stimulating peripheral glucose uptake, especially by skeletal muscle and fat, and by inhibiting hepatic glucose production; insulin inhibits lipolysis and proteolysis and enhances protein synthesis; targets include skeletal muscle, liver, and adipose tissue
5.TAB. Digoxin
mechanism: Digoxin has two principal mechanisms of action which are selectively employed depending on the indication:
Positive Ionotropic: It increases the force of contraction of the heart by reversibly inhibiting the activity of the myocardial Na-K ATPase pump,
an enzyme that controls the movement of ions into the heart.
6. Hypoglycemia symptoms explained
7. Watch for any bleeding manifestations like Petechiae, Bleeding gums.
8. APTT and INR are ordered on a regular basis when a person is taking the anticoagulant drug warfarin to make sure that the drug is producing the desired effect.
Question 3
What is the pathogenesis of renal involvement due to heart failure (cardio renal syndrome)? Which type of cardio renal syndrome is this patient?
Answer
cardiorenal syndrome type 4 is seen in this patient.
Question 4
What are the risk factors for atherosclerosis in this patient?
Answer
effect of hypertention
They can also impair blood vessels' ability to relax and may stimulate the growth of smooth muscle cells inside arteries. All these changes can contribute to the artery-clogging process known as atherosclerosis.
Question 5
Why was the patient asked to get those APTT, INR tests for review?
Answer
APTT and INR are ordered on a regular basis when a person is taking the anticoagulant drug warfarin to make sure that the drug is producing the desired effect.
Here, an INR of 3-4.5 is recommended. Warfarin should be started in conjunction with heparin or low molecular weight heparin when the diagnosis of venous thromboembolism is confirmed, although local protocols may vary in their starting doses and titration schedule.
CASE 13
67 year old patient with acute coronary syndrome
Question 1
What is the evolution of the symptomatology in this patient in terms of an event timeline and where is the anatomical localization for the problem and what is the primary etiology of the patient's problem?
Answer
TIMELINE OF EVENTS-
• Diabetes since 12 years - on medication
• Heart burn like episodes since an year- relieved without medication
• Diagnosed with pulmonary TB 7 months ago- completed full course of treatment, presently sputum negative.
• Hypertension since 6 months - on medication
• Shortness of breath since half an hour-SOB even at rest
Anatomical localisation - Cardiovascular system
Etiology: The patient is both Hypertensive and diabetic , both these conditions can cause
- Atherosclerosis: there is build up of fatty and fibrous material inside the wall of arteries.(PLAQUE)
Question 2
What are mechanism of action, indication and efficacy over placebo of each of the pharmacological and non pharmacological interventions used for this patient?
Answer
Pharmacological interventions:
TAB MET XL 25 MG/STAT-contains Metoprolol as active ingredient
MOA: METOPROLOL is a cardiselective beta blocker
Beta blockers work by blocking the effects of the hormone epinephrine, also known as adrenaline. Beta blockers cause your heart to beat more slowly( negative chronotropic effect)
and with less force( negative inotropic effect). Beta blockers also help open up your veins and arteries to improve blood flow.
Indications: it is used to treat Angina, High blood pressure and to lower the risk of hear attacks .
EFFICACY STUDIES.
Patients were randomized to one of four treatment arms: placebo or ER metoprolol (0.2 mg/kg, 1.0 mg/kg, or 2.0 mg/kg). Data were analyzed on 140 intent-to-treat patients.
Results: mean baseline BP was 132/78 +/- 9/9 mmHg. Following 4 weeks of treatment, mean changes in sitting BP were: placebo = -1.9/-2.1 mmHg; ER metoprolol 0.2 mg/kg = -5.2/-3.1 mmHg; 1.0 mg/kg = -7.7/-4.9 mmHg; 2.0 mg/kg = -6.3/-7.5 mmHg. Compared with placebo, ER metoprolol significantly reduced systolic blood pressure (SBP) at the 1.0 and 2.0 mg/kg dose (P = .027 and P = .049, respectively), reduced diastolic blood pressure (DBP) at the 2.0 mg/kg dose (P = .017), and showed a statistically significant dose response relationship for the placebo-corrected change in DBP from baseline. There were no serious adverse events or adverse events requiring study drug discontinuation among patients receiving active therapy.
Non pharmacological intervention advised to this patient is: PERCUTANEOUS CORONARY INTERVENTION.
Percutaneous Coronary Intervention is a non-surgical procedure that uses a catheter (a thin flexible tube) to place a small structure called a stent to open up blood vessels in the heart that have been narrowed by plaque buildup ( atherosclerosis).
Question 3
What are the indications and contraindications for PCI?
Answer
INDICATIONS:
Acute ST-elevation myocardial infarction (STEMI)
Non–ST-elevation acute coronary syndrome (NSTE-ACS)
Unstable angina.
Stable angina.
Anginal equivalent (eg, dyspnea, arrhythmia, or dizziness or syncope)
High risk stress test findings.
CONTRAINDICATIONS:
Intolerance for oral antiplatelets long-term.
Absence of cardiac surgery backup.
Hypercoagulable state.
High-grade chronic kidney disease.
Chronic total occlusion of SVG.
An artery with a diameter of <1.5 mm.
Question 4
What happens if a PCI is performed in a patient who does not need it? What are the harms of overtreatment and why is research on overtesting and overtreatment important to current healthcare systems?
Answer
Although PCI is generally a safe procedure , it might cause serious certain complications like
A)Bleeding
B) Blood vessel damage
C) Allergic reaction to the contrast dye used
D) Arrhythmias
E) Need for emergency coronary artery bypass grafting .
Because of all these complications it is better to avoid PCI in patients who do not require it.
⁃ OVER TESTING AND OVER TRAETMENT HAVE BECOME COMMMIN IN TODAY’S MEDICAL PRACTICE.
⁃ Research on overtesting and overtreatment is important as they are more harmful than useful.
Harms to patients
. Performing screening tests in patients with who at low risk for the disease which is being screened.
For example:Breast Cancer Screenings Can Cause More Harm Than Good in Women Who Are at Low Risk. A harmless lump or bump could incorrectly come up as cancer during routine breast screenings. This means that some women undergo surgery, chemotherapy or radiation for cancer that was never there in the first place.
.Overuse of imaging techniques such as X- RAYS AND CT SCANS as a part of routine investigations.
Overuse of imaging can lead to a diagnosis of a condition that would have otherwise remained irrelevant - OVERDIAGNOSIS.
Also the adverse effects due to this are more when compared to the benefits.
.Overdiagnosis through overtesting can psychologically harm the patient.
Hospitalizations[41] for those with chronic conditions who could be treated as outpatients[ can lead to economic burden and a feeling of isolation.
Harms to health care systems
The use of expensive technologies and machineries are causing burden on health care systems.
CASE 14
A 60year old Male patient, came to the OPD with the Chief complaint of chest pain since 3 days and giddiness and profuse sweating since morning
Question 1
What is the evolution of the symptomatology in this patient in terms of an event timeline and where is the anatomical localization for the problem and what is the primary etiology of the patient's problem?
Answer
the anatomical location ofetiology is BLOOD VESSELS.
*myocardial infarction is usually due to thrombotic occlusion of a coronary vessel caused by rupture of a vulnerable plaque. Ischemia induces profound metabolic and ionic perturbations in the affected myocardium and causes rapid depression of systolic function
Question 2
What are mechanism of action, indication and efficacy over placebo of each of the pharmacological and non pharmacological interventions used for this patient?
Answer
PHARMACOLOGICAL INNTERVENTION
1.TAB. ASPIRIN
mechanism:Aspirin inhibits platelet function through irreversible inhibition of cyclooxygenase (COX) activity. Until recently, aspirin has been mainly used for primary and secondary prevention of arterial antithrombotic events.
2.TAB ATORVAS
mechanism:Atorvastatin competitively inhibits 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-coenzyme A (HMG-CoA) reductase. By preventing the conversion of HMG-CoA to mevalonate, statin medications decrease cholesterol production in the liver.
3.TAB CLOPIBB
mechanism:The active metabolite of clopidogrel selectively inhibits the binding of adenosine diphosphate (ADP) to its platelet P2Y12 receptor and the subsequent ADP- mediated activation of the glycoprotein GPIIb/IIIa complex, thereby inhibiting platelet aggregation. This action is irreversible.
4.INJ HAI
mechanism:Regulates glucose metabolism
Insulin and its analogues lower blood glucose by stimulating peripheral glucose uptake, especially by skeletal muscle and fat, and by inhibiting hepatic glucose production; insulin inhibits lipolysis and proteolysis and enhances protein synthesis; targets include skeletal muscle, liver, and adipose tissue
5.ANGIOPLASTY
mechanism:Angioplasty, also known as balloon angioplasty and percutaneous transluminal angioplasty (PTA), is a minimally invasive endovascular procedure used to widen narrowed or obstructed arteries or veins, typically to treat arterial atherosclerosis.
Question 3
Did the secondary PTCA do any good to the patient or was it unnecessary?
Answer
the second PCI was NOT necessary in this patient.
PCI performed from 3 to 28 days after MI does not decrease the incidence of death, reinfarction or New York Heart Association (NYHA) class IV heart failure but it is associated with higher rates of both procedure-related and true ST elevation reinfarction.3 A retrospective analysis of the clinical data revealed The Thrombolysis in Myocardial Infarction (TIMI) Risk Score of 4 predicting a 30-day mortality of 7.3% in this patient. Late PCI leads to the increased risks of periprocedural complications, long-term bleeding, and stent thrombosis.
The high incidence of CAD and the increasing need for PCI provides an opportunity to evaluate its appropriate use and highlight potential overuse. PCI is frequently reported to be overused and inappropriately recommended. Behnke et al defined overuse as ‘use of unnecessary care when alternatives may produce similar outcomes, resulting in a higher cost without increased value’.Overuse causes a heavy financial burden on people living in countries, where fee-for-service and ill-regulated private healthcare provides much of the patient care. As a result, cost of healthcare increases and causes potential harm to the patients.
CASE 15
A case of cardiogenic shock. An 87 year old male patient has presented with the complaints of shortness of breath since 3 days constipation since 3 days decreased urine output since 2 days
Question 1
How did the patient get relieved from his shortness of breath after i.v fluids administration by rural medical practitioner?
Answer
Because of the fluid loss occurred to the patient
there is decreased preload- so, SOB occurred due to decreased CO
IV fluids administered- there is increased preload- SOB decreased due to better of cardiac output.
Question 2
What is the rationale of using torsemide in this patient?
Answer
Torsemide used to relieve abdominal distension.
Question 3
Was the rationale for administration of ceftriaxone? Was it prophylactic or for the treatment of UTI?
Answer
IT IS THE TREATMENT FOR UTI
Rationale- Used for any bacterial infection.
GASTROENTEROLOGY AND PULMONOLOGY
CASE 16
A 33 year old man with pancreatitis, pseudocyst and left broncho-pleural fistula
Question 1
What is the evolution of the symptomatology in this patient in terms of an event timeline and where is the anatomical localization for the problem and what is the primary etiology of the patient's problem?
Answer
Evolution of symptomatology
H5 years back-1st episode of pain abdomen and vomitings
Stopped taking alcohol for 3 years
1 year back 5 to 6 episodes of pain abdomen and vomitings after starting to drink alcohol again
20 days back increased consumption of toddy intake
Since 1 week pain abdomen and vomiting
Since 4 days fever constipation and burning micturition
Anatomical localisation: Pancreas and left lung
Alcohol and its metabolites produce changes in the acinar cells, which may promote premature intracellular digestive enzyme activation thereby predisposing the gland to autodigestive injury. Pancreatic stellate cells (PSCs) are activated directly by alcohol and its metabolites and also by cytokines and growth factors released during alcohol-induced pancreatic necroinflammation. Activated PSCs are the key cells responsible for producing the fibrosis of alcoholic chronic pancreatitis
Question 2
What is the efficacy of drugs used along with other non pharmacological treatment modalities and how would you approach this patient as a treating physician?
Answer
Non pharmacological interventions : drains ( malecot & icd )
* Even i as a treating physician will follow the same approach
CASE 17
Case discussion on 25 yr old male with epigastric pain
Question 1
What is causing the patient's dyspnea? How is it related to pancreatitis?
Answer
the cause of dyspnea might be PLEURAL EFFUSION
Question 2
Name possible reasons why the patient has developed a state of hyperglycemia.
Answer
*This hyperglycemia could thus be the result of a hyperglucagonemia secondary to stress
* the result of decreased synthesis and release of insulin secondary to the damage of pancreatic β-cells
* elevated levels of catecholamines and cortisol
Question 3
What is the reason for his elevated LFTs? Is there a specific marker for Alcoholic Fatty Liver disease?
Answer
LFT are increased due to hepatocyte injury
*If the liver is damaged or not functioning properly, ALT can be released into the blood. This causes ALT levels to increase. A higher than normal result on this test can be a sign of liver damage.
*elevated alanine transaminase (ALT) and aspartate transaminase (AST), usually one to four times the upper limits of normal in alcoholic fatty liver.
The reasons for a classical 2:1 excess of serum AST activity compared to serum ALT activity in alcoholic hepatitis have been attributed to
(i) decreased ALT activity most likely due to B6 depletion in the livers of alcoholics
(ii) mitochondrial damage leading to increased release of mAST in serum.
Question 4
What is the line of treatment in this patient?
Answer
Plan of action and Treatment:
Investigations:
✓ 24 hour urinary protein
✓ Fasting and Post prandial Blood glucose
✓ HbA1c
✓ USG guided pleural tapping
Treatment:
• IVF: 125 mL/hr
• Inj PAN 40mg i.v OD
• Inj ZOFER 4mg i.v sos
• Inj Tramadol 1 amp in 100 mL NS, i.v sos
• Tab Dolo 650mg sos
• GRBS charting 6th hourly
• BP charting 8th hourly
CASE 18
A 45 year old Female patient with Fever, Pain abdomen, Decreased Urine output and Abdominal distension
Question 1
What is the most probable diagnosis in this patient?
Answer
Differential Diagnosis:
• Ruptured Liver Abscess.
• Organized collection secondary to Hollow viscous Perforation.
• Organized Intraperitoneal Hematoma.
• Free fluid with internal echoes in Bilateral in the Subdiaphragmatic space.
• Grade 3 RPD of right Kidney
àThe most probably diagnosis is there is abdominal hemorrhage. This will give reasoning to the abdominal distention, and the blood which is aspirated.
Question 2
What was the cause of her death?
Answer
After leaving the hospital, the patient went to Hyderabad and underwent an emergency laparotomy surgery. The patient passed away the next day. Cause of her death can be due to complications of laparotomy surgery such as, hemorrhage (bleeding), infection, or damage to internal organs.
Question 3
Does her NSAID abuse have something to do with her condition? How?
Answer
NSAID-induced renal dysfunction has a wide spectrum of negative effects, including decreased glomerular perfusion, decreased glomerular filtration rate, and acute renal failure. Chronic NSAIDs use has also been related to hepatotoxicity. While the major adverse effects of NSAIDs such as gastrointestinal mucosa injury are well known, NSAIDs have also been associated with hepatic side effects ranging from asymptomatic elevations in serum aminotransferase levels and hepatitis with jaundice to fulminant liver failure and death.
NEPHROLOGY AND UROLOGY
CASE 19
Post TURP with non oliguric ATN
A 52 yr old male patient who is a farmer by occupation
Presented to hospital on 17 May 2021 with Chief Complaints of
SOB since 4 days
Burning micturition since 4 days
Fever since 2 days
Question 1
what could be the cause for his SOB
Answer
His sob was is due to Acidosis which was caused by Diuretics
Question 2
Reason for Intermittent Episodes of drowsiness
Answer
Hyponatremia was the cause for his drowsiness
why did he complaint of fleshy mass like passage in urine
Answer
plenty of pus cells in his urine passage appeared as
fleshy mass like passage to him
Question 4
What are the complications of TURP that he may have had ?
Answer
Difficulty micturition
Electrolyte imbalances
Infection
CASE 20
An Eight year old with Frequent Urination
Question 1
Why is the child excessively hyperactive without much of social etiquettes ?
Answer
Attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) is a neurodevelopmental disorder characterized by inattention, or excessive activity and impulsivity, which are otherwise not appropriate for a person's age
For a diagnosis, the symptoms have to be present for more than six months, and cause problems in at least two settings (such as school, home, work, or recreational activities).
Question 2
Why doesn't the child have the excessive urge of urination at night time ?
Answer
Since the child doesn’t have excessive urge of urination at night but at day there might be a psychiatry related condition
1. Psychosomatic disorder
2. Undiagnosed anxiety disorder
Question 3
How would you want to manage the patient to relieve him of his symptoms?
bacterial kidney infection, the typical course of treatment is antibiotic and painkiller therapy.
Answer
If the cause is an overactive bladder, a medication known as an anticholinergic may be used. These prevent abnormal involuntary detrusor muscle contractions from occurring in the wall of the bladder
To treat attention deficit hyperactivity disorder:
For children 6 years of age and older, the recommendations include medication and behavior therapy together — parent training in behavior management for children up to age 12 and other types of behavior therapy and training for adolescents. Schools can be part of the treatment as well.
Methylphenidate A stimulant and a medication used to treat Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder. It can make you feel very ‘up’, awake, excited, alert and energised, but they can also make you feel agitated and aggressive. They may also stop you from feeling hungry.
Amphetamine belongs to a class of drugs known as stimulants. It can help increase your ability to pay attention, stay focused on an activity, and control behavior problems. It may also help you to organize your tasks and improve listening skills.
INFECTIOUS DISEASES( HI virus , mycobacterium, gastroenterology, pulmonology)
CASE 21
A 40 year old lady who works in cotton fields came to the hospital with the chief complaints of difficulty in swallowing , fever and cough , since 2 months
Question 1
Which clinical history and physical findings are characteristic of tracheo esophageal fistula?
Answer
Cough since 2 months on taking food and liquids
•difficulty in swallowing since 2 month . It was initially difficult only with solids but then followed by liquids also.
•laryngeal crepitus- positive
These favour for tracheo esophageal.fistula
Question 2
What are the chances of this patient developing immune reconstitution inflammatory syndrome? Can we prevent it?
Answer
Immune reconstitution inflammatory syndrome (IRIS) represents the worsening of a recognized (paradoxical IRIS) or unrecognized (unmasking IRIS) pre-existing infection in the setting of improved immunologic function.
The most effective prevention of IRIS would involve initiation of ART before the development of advanced immunosuppression. IRIS is uncommon in individuals who initiate antiretroviral treatment with a CD4+ T-cell count greater than 100 cells/uL.
Aggressive efforts should be made to detect asymptomatic mycobacterial or cryptococcal disease prior to the initiation of ART, especially in areas endemic for these pathogens and with CD4 T-cell counts less than 100 cells/uL.
Two prospective randomized studies are evaluating prednisone and meloxicam for the prevention of paradoxical TB IRIS.
INFECTIOUS DISEASES AND HEPATOLOGY
CASE 22
A 52 yr old male patient who is a farmer by occupation
Presented to hospital on 17 May 2021 with Chief Complaints of
SOB since 4 days
Burning micturition since 4 days
Fever since 2 days
Question 1
do you think drinking locally made alcohol cause liver abscess in this patient due to predisposing factors present in it ? What could be the cause in this patient?
Answer
yes, it could be due to intake of contaminated toddy
Question 2
what is the etiopathogenesis of liver abscess in a chronic alcoholic patient?(since 30 yrs - 1 bottle/day)
Answer
according to some studies, alcoholism mainly consuming locally prepared alcohol plays a major role as a predisposing factor for the formation of liver abscesses that is both amoebic as well as pyogenic liver abscess because of the adverse effects of alcohol over the Liver. It is also proven that Alcoholism is never an etiological factor for the formation of liver abscess.
Question 3
is liver abscess is more common in right lobe?
Answer
yes right lobe is involved due to its moreblood supply
Question 4
what are the indications for usg guided aspiration of liver abscess
Answer
Indications for USG guided aspiration of liver abscess
1. Large abscess more than 6cms
2. Left lobe abscess
3.Caudate lobe abscess
4. Abscess which is not responding to drugs
CASE 23
A case of liver abcess
A 21 yr old male student, came to the hospital with the cheif complaints of abdominal pain since 20 days and fever since 18 days
Question 1
Cause of liver abcess in this patient ?
Answer
Here ; the cause of liver abcess is :
Amoebic liver abcess (ALA ) seen commonly in the tropics is predominantly confined to adult males, especially those who consume locally brewed alcohol, although intestinal amoebiasis occurs in all age groups and in both genders.
It has been argued that socioeconomic factors and poor sanitary conditions are the primary culprits that casually link alcohol to ALA.
However , there has emerged an abundance of data that implicates alcohol in a more causal role in facilitating the extraintestinal invasion of the infective protozoan and the subsequent development of ALA.
Hence the consumption of locally made alcohol ( toddy ) is the most likely cause of Liver abcess in this patient.
Question 2
How do you approach this patient ?
Answer
The patient is well managed by treating team ; even me will follow the same approach.
Question 3
Why do we treat here ; both amoebic and pyogenic liver abscess?
Answer
Considering the following factors:
1) Age and gender of patient: 21 years ( young ) and male.
2) Single abcess.
3) Right lobe involvement.
The abcess is most likely AMOEBIC LIVER ABSCESS …
But most of the patients with amoebic liver abcess have no bowel symptoms, examination of stool for ova and parasite and antigen testing is insensitive and insensitive and not recommended.
And considering the risk factors associated with aspiration for pus culture:
1) Sometimes ; abcess is not accessible for aspiration if it is in posterior aspect or so.
2) Sometimes ; it has thin thinwall which may rupture if u aspirate.
3) Sometimes ; it is unliquefied.
There how can u confirm whether it is pyogenic/ amoebic , so we treat them both empirically in clinical practice
Question 4
Is there a way to confirmthe definitive diagnosis in this patient?
Answer
Yes in a high resource setting cause of liver abscess is usually determined using multiple diagnostic strategies , including blood cultures , entamoeba serology , liver abscess aspirate for culture and molecular and antigen testing.
INFECTIOUS DISEASES( MUCOURMYCOSIS, OPHTHALMOLOGY, OTORHINOLARYNOLOGY , NEUROLOGY)
CASE 24
50/Male came with altered sensorium
Question 1
What is the evolution of the symptomatology in this patient in terms of an event timeline and where is the anatomical localization for the problem and what is the primary aetiology of the patient's problem?
Answer
1. 3 years ago- diagnosed with hypertension
2. 21 days ago- received vaccination at local PHC which was followed by fever associated with chills and rigors, high grade fever, no diurnal variation which was relieved on medication
3. 18 days ago- complained of similar events and went to the the local hospital, it was not subsided upon taking medication(antipyretics)
4. 11 days ago - c/o Generalized weakness and facial puffiness and periorbital oedema. Patient was in a drowsy state
5. 4 days ago-
a. patient presented to casualty in altered state with facial puffiness and periorbital oedema and weakness of right upper limb and lower limb
b. towards the evening patient periorbital oedema progressed
c. serous discharge from the left eye that was blood tinged
d. was diagnosed with diabetes mellitus
6. patient was referred to a government general hospital
7. patient died 2 days ago
patient was diagnosed with diabetic ketoacidosis and was unaware that he was diabetic until then. This resulted in poorly controlled blood sugar levels. The patient was diagnosed with acute oro rhino orbital mucormycosis . rhino cerebral mucormycosis is the most common form of this fungus that occurs in people with uncontrolled diabetes the fungus enters the sinuses from the environment and then the brain.
The patient was also diagnosed with acute infarct in the left frontal and temporal lobe. Mucormycosis is associated with the occurrence of CVA
Question 2
What is the efficacy of drugs used along with other non-pharmacological treatment modalities and how would you approach this patient as a treating physician?
Answer
The proposed management of the patient was –
1. inj. Liposomal amphotericin B according to creatinine clearance
2. 200mg Iitraconazole was given as it was the only available drug which was adjusted to his creatinine clearance
3. Deoxycholate was the required drug which was unavailable
I. Management of diabetic ketoacidosis –
(a) Fluid replacement- The fluids will replace those lost through excessive urination, as well as help dilute the excess sugar in blood.
(b) Electrolyte replacement-The absence of insulin can lower the level of several electrolytes in blood. Patient will receive electrolytes through a vein to help keep the heart, muscles and nerve cells functioning normally.
(c) Insulin therapy- Insulin reverses the processes that cause diabetic ketoacidosis. In addition to fluids and electrolytes, patient will receive insulin therapy
Question 3
What are the postulated reasons for a sudden apparent rise in the incidence of mucormycosis in India at this point of time?
Answer
Mucormycosis is may be being triggered by the use of steroids, a life-saving treatment for severe and critically ill Covid-19 patients. Steroids reduce inflammation in the lungs for Covid-19 and appear to help stop some of the damage that can happen when the body's immune system goes into overdrive to fight off coronavirus. But they also reduce immunity and push up blood sugar levels in both diabetics and non-diabetic Covid-19 patients.
With the COVID-19 cases rising in India the rate of occurrence of mucormycosis in these patients is increasing
INFECTIOUS DISEASES COVID 19
As these patients are currently taking up more than 50% of our time we decided to make a separate log link here:
for this question that contains details of many of our covid 19 patients documented over this month and we would like you to:
1) Sort out these detailed patient case report logs into a single web page as a master chart
2) In the master chart classify the patient case report logs into mild, moderate severe and
3) indicate for each patient, the day of covid when their severity changed from moderate to severe or vice versa recognized primarily through increasing or decreasing oxygen requirements
4) Indicate the sequence of specific terminal events for those who died with severe covid (for example, altered sensorium, hypotension etc).
INFECTIOUS DISEASES COVID 19 CASES
MEDICINE EDUCATION
Experiential learning is a very important method of Medical education and while the E logs of the students in the questions above represent partly their and their patient's experiences, reflective logging of one's own experiences is a vital tool toward competency development in medical education and research. A sample answer to this last assignment around sharing your experience log of the month can be seen in the link below but while this is by a student onsite in hospital and not locked down at home we would be very interested to learn about your telemedical learning experiences from our hospital as well as community patients over the last month even while locked down at home:https://onedrive.live.com/view.aspx?resid=4EF578BAE67BA469!4180&ithint=file%2cdocx&authkey=!AOy7BpRTn42DBMo.
Listening to classes online and gaining practical knowledge is difficult but ,with initial hesitation anxiety and inferiority complex where all found out to be passing clouds when I made my first e-log Being home and listening to classes online and few hours of lessons and days of learning effortlessly made us learn things in matter of minutes to hours. This is the best thing to have happened in the field of learing, there have been dreams about solving cases and finding answers. All thanks to Rakesh biswas sir and post graduates ,interns ,medicine department for making us to learn in such a effective and healthy way.

















































Comments
Post a Comment